Non-neutral Plasma
Penning Trap (for a single particle)
A single charged particle can be confined with static magnetic field for the radial confinement and electrostatic field for the axial confinement. If the electrostatic field is the solution of Laplace equation in the vacuum (it becomes harmonic potential), the trap is called "Penning trap" which is used for precise measurement of g-factor, charge to mass ratio, and so on.
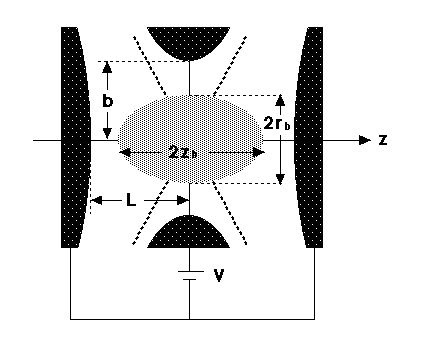
Malmberg Trap (for a non-neutral plasma)
Malmberg Trap was developed to confine much more charged particles in a trap. The electrostatic potential is not harmonic any more.When charged particles are acumulated, it shows some specific features as a plasma, which is called "Non-neutral plasma". Theoretically, the rigid rotor equilibrium is expected for a non-neurtal plasma as shown below. The extreme confinement time of the non-neutral plasma is suitable to reveal various basic features (diffusion, heat flow, etc.)of plasmas in equilibrium.
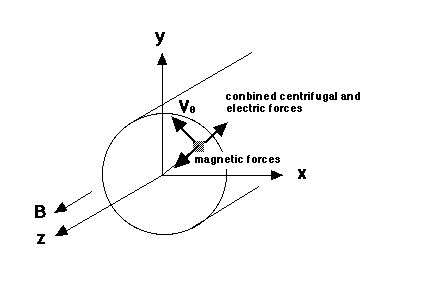
In the rigid rotor equilibrium, a non-neutral plasma column with a constant density n rotates around the axis of symmetry with either higher or lower rotation frequency \omega_r. It should be noted that there is the maximum density n_B (Brilloin density limit) for the rigid rotor equilibrium at a fixed magnetic field.
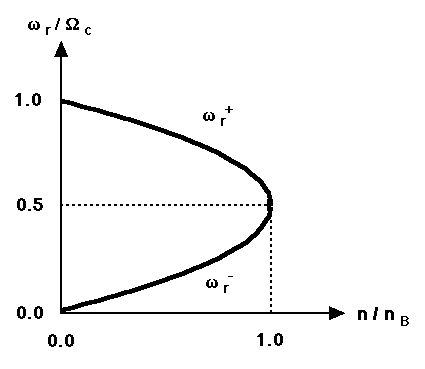
I studied nonlinear electrostatic oscillations in a non-neutral electron plasma column (details).
Multi-Ring Electrode trap (for application)
When many charged particles should be confined in a harmonic potential, Multi-Ring Electrode trap is the practical solution in some cases. A spheroidal non-neutral plasma in a harmonic potential can be diagnosed non-destructively. Although there is an image charge effect, the particle number is infered by monitering the first order electrostatic harmonic oscillation with a tank circuit and the density can be checked by monitering the frequency shift of the second order electrostatic harmonic oscillation. In fact, the Multi-Ring Electrode trap is suitable for the effective electron cooling of high energy antiprotons in a trap, because it can confine high density electrons in a large volume (details).
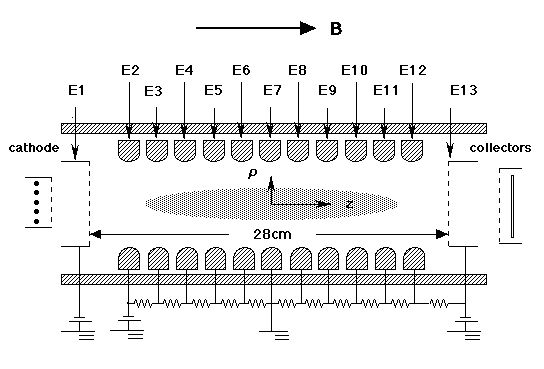
References
D.Wineland, P.Ekstrom, and H.G.Dehmelt, Phys.Rev.Lett. 31 (1973) 1279
J.H.Malmberg and J.S.deGrassie, Phys.Rev.Lett. 35 (1975) 577
H.Higaki and A.Mohri, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36 Pt.1 (1997) 5300
"The Physics of Non-neutral Plasmas", R.C.Davidson, Addison-Weseley, Redwood City, 1991
Back to the top