Laboratory of Neurometabolism, Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life, Hiroshima University, Japan
Principal Investigator
Kazuyoshi Ukena (Distinguished Professor)
Our recent research of a novel brain neuropeptide
Throughout history, our ancestors needed to accumulate fat to survive during times when food sources were scarce. However, for most people in the modern age, food is abundant and eating too much is a major cause of weight gain, obesity and diseases affecting the metabolism. Obesity in particular, can lead to diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
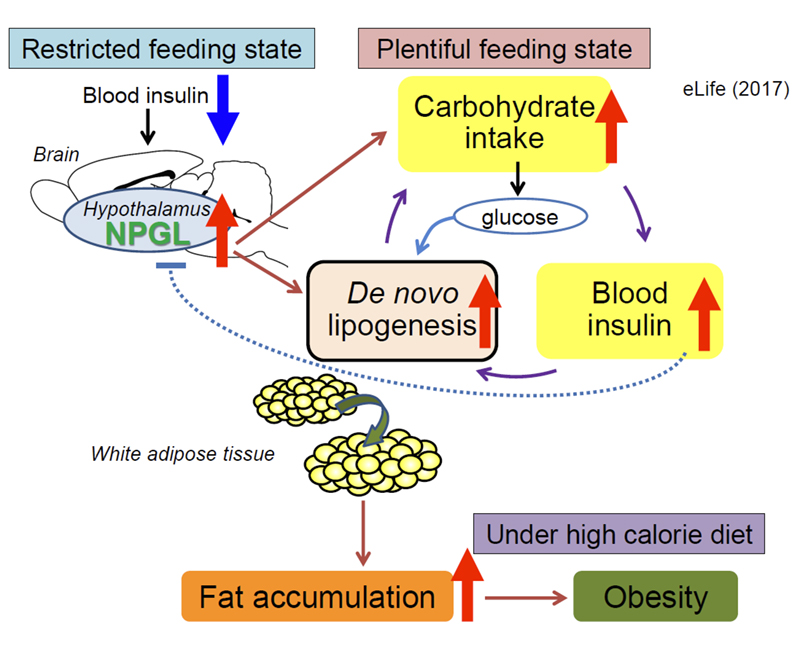
Hunger and appetite are regulated by proteins and other chemicals that act as messengers, for example insulin, and a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. However, the full mechanisms that regulate these sensations remain unclear. Recently, we have discovered a small protein called neurosecretory protein GL (NPGL; 80 amino acid residues) in a part of the hypothalamus of birds and mammals (BBRC 2014, Endocrinology 2017, eLife 2017). However, it was not known if NPGL plays a role in regulating eating habits and weight gain.
We have found that NPGL is produced in the hypothalamus of rats and is regulated by diet and insulin. When the gene for NPGL was manipulated to produce too much of the small protein, rats fed a high calorie diet started to eat more, and gained more weight and body fat. Adding additional NPGL to their brains had the same effect. When the animals were fed a normal diet, NPGL only moderately affected how much they ate, but it substantially increased how much fat they produced. We also observed that when animals were starved and insulin levels were low, the rats started to produce more NPGL. These results suggest that NPGL plays a role in fat storage when energy sources are limited, and can contribute to obesity when too much NPGL is produced in animals on a high calorie diet. We reported these results on the Journal, eLife (2017).
These findings indicate that NPGL could be an additional brain chemical that regulates hunger and fat storage in mammals. A next step will be to reveal the specific mechanisms by which NPGL regulates overeating and fat accumulation. We hope that these findings will further advance the study and treatment of obesity and obesity-related diseases.
Related publications
- Narimatsu Y, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Fukumura K, Shikano K, Furumitsu M, Morishita M, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Hypothalamic overexpression of neurosecretory protein GL leads to obesity in male C57BL/6J mice. Neuroendocrinology 112:606–620 (2022) (This paper was chosen for the Editor’s Choice article)
- Narimatsu Y, Matsuura D, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Neurosecretory protein GL promotes normotopic fat accumulation in male ICR mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:6488 (2022)
- Kato M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Narimatsu Y, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Effect of stressors on the mRNA expressions of neurosecretory protein GL and neurosecretory protein GM in chicks. Front. Physiol. 13:860912 (2022)
- Naito M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Moriwaki S, Narimatsu Y, Kato M, Furumitsu M, Miyamoto Y, Esumi S, Ukena K*. Immunohistochemical analysis of neurotransmitters in neurosecretory protein GL-producing neurons of the mouse hypothalamus. Biomedicines 10:454 (2022)
- Narimatsu Y, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Naito M, Moriwaki S, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Neurosecretory protein GL accelerates liver steatosis in mice fed medium-fat/medium-fructose diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:2071 (2022)
- Kato M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E*, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. A novel hypothalamic factor, neurosecretory protein GM, causes fat deposition in chicks. Front. Physiol. 12:747473 (2021)
- Fukumura K, Narimatsu Y, Moriwaki S, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Overexpression of the gene encoding neurosecretory protein GL precursor prevents excessive fat accumulation in the adipose tissue of mice fed a long-term high-fat diet. Molecules 26:6006 (2021)
- Narimatsu Y, Fukumura K, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Mimura A, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Subcutaneous infusion of neurosecretory protein GL promotes fat accumulation in mice. Heliyon 7:e07502 (2021)
- Fukumura K, Shikano K, Narimatsu Y, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Naito M, Ukena K*. Effects of neurosecretory protein GL on food intake and fat accumulation under different dietary nutrient compositions in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 85:1514-1520 (2021)
- Fukumura K, Narimatsu Y, Moriwaki S, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Effects of overexpression of neurosecretory protein GL-precursor gene on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:4681 (2021)
- Kadota A, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Fukumura K, Shikano K, Narimatsu Y, Furumitsu M, Ukena K*. Effects of irregular feeding on the daily fluctuations in mRNA expression of the neurosecretory protein GL and neurosecretory protein GM genes in the mouse hypothalamus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:2109 (2021)
- Shikano K, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Saito T, Narimatsu Y, Kadota A, Furumitsu M, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Neurosecretory protein GL induces fat accumulation in mice. J. Endocrinol. 244:1-12 (2020)
- Shikano K, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Kato M, Furumitsu M, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Neurosecretory protein GL induces fat accumulation in chicks. Front. Endocrinol. 10:392 (2019)
- Shikano K, Bessho Y, Kato M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Taniuchi S, Furumitsu M, Tachibana T, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Localization and function of neurosecretory protein GM, a novel small secretory protein, in the chicken hypothalamus. Sci. Rep. 8:704 (2018)
- Shikano K, Taniuchi S, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Chronic subcutaneous infusion of neurosecretory protein GM increases body mass gain in chicks. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 265:71-76 (2018)
- Ukena K*. Avian and murine neurosecretory protein GL participates in the regulation of feeding and energy metabolism (Review). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 260:164-170 (2018)
- Shikano K, Kato M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Matsuura D, Masuda K, Tachibana T, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Effects of chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of neurosecretory protein GL on body mass and food and water intake in chicks. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 256:37-42 (2018)
- Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Shikano K, Kondo K, Taniuchi S, Furumitsu M, Ochi Y, Sasaki T, Okamoto S, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Minokoshi Y, Ukena K*. Neurosecretory protein GL stimulates food intake, de novo lipogenesis, and onset of obesity. eLife 6:e28527 (2017)
- Matsuura D, Shikano K, Saito T, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Ochi Y, Sato M, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Ukena K*. Neurosecretory protein GL, a hypothalamic small secretory protein, participates in energy homeostasis in male mice. Endocrinology 158:1120-1129 (2017) (This paper was chosen for the Endocrine Society’s thematic issue on neuroendocrinology 2018)
- Masuda K, Furumitsu M, Ooyama H, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Ukena K*. Synthesis of neurosecretory protein GM composed of 88 amino acid residues by native chemical ligation. Tetrahedron Lett. 57:804-807 (2016)
- Masuda K, Furumitsu M, Taniuchi S, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Ukena K*. Production and characterization of neurosecretory protein GM using Escherichia coli and Chinese Hamster Ovary cells. FEBS Open Bio 5:844-851 (2015)
- Masuda K, Ooyama H, Shikano K, Kondo K, Furumitsu M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Ukena K*. Microwave-assisted solid-phase peptide synthesis of neurosecretory protein GL composed of 80 amino acid residues. J. Pept. Sci. 21:454-460 (2015)
- Ukena K*, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Taniuchi S, Bessho Y, Maejima S, Masuda K, Shikano K, Kondo K, Furumitsu M, Tachibana T. Identification of a cDNA encoding a novel small secretory protein, neurosecretory protein GL, in the chicken hypothalamic infundibulum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 446:298-303 (2014)
Related Sites
- [Research] Recently discovered brain chemical “NPGL” controls appetite and body fat composition – beneficial for our ancestors; potential cause of obesity pandemic
- [Research] New appetite control mechanism found in brain – reason food looks even better when dieting
- [Interview] 2020 An interview with Distinguished Professor Kazuyoshi Ukena
- [Interview] 2020 Talk About Research in Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life, Hiroshima University
- [Interview] 2017 An interview with Distinguished Researcher Kazuyoshi Ukena
- [Profile] Database of Hiroshima University



