[iot][arduino][breeding]Arduinoで水槽の温度管理
安価なマイコン基盤であるArduinoを使って、水槽の温度をクラウドサービスを利用してモニタリングし、さらに一定の温度から外れるとアラートをメールしてくれるシステムを作りました。
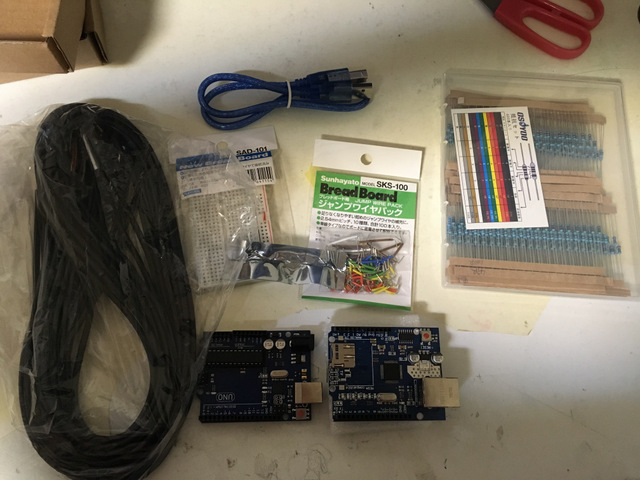
購入したのは、以下の機材
・Arduino Uno (のクローンの安物、1,000円程度)
・Ethernet Shield for Arduino Uno (のクローンの安物、1,500円程度)
・温度センサー DS18B20
・ブレッドボード
・金属皮膜抵抗器
・ジャンプワイヤキット

ブレッドボードにセンサーの三芯線とArduinoの5V電源、GRD、デジタル入力からのジャンパ線を刺し、サンプルのスケッチを参考に手直しを加えたら完成。
今のところ、室温と4つの水槽の水温(=5つの温度プローブ)を5分ごとに取得し、これをAT&Tのクラウドリソース、m2xにアップロードし、モニタリングしています(実際のサイト)。設定温度から上下1℃以上変動すると、Herokuに置いたアラートが作動してラボのメンバーにメールが通知されるようになっています。今のところ設置してから二か月以上、安定して動作しています。
スケッチは下記のもの。いろいろ試行錯誤した結果、MSTimer2を利用するのが最も安定しているようです。
#include <MsTimer2.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
#define TEMPERATURE_PRECISION 12
#define ARDUINO_PLATFORM
#include "M2XStreamClient.h"
// MAC address for your Ethernet shield
byte mac[] = { NICのMACアドレス };
// Set the static IP address to use if the DHCP fails to assign
byte ip[] = { NICのIPアドレス };
byte dns_adress[] = { DNSアドレス };
byte gateway[] = { ゲートウェイアドレス };
byte subnet[] = { サブネットマスク };
char deviceId[] = "m2xのデバイスID"; // Device you want to push to
char m2xKey[] = "m2xのキー"; // Your M2X access key
char streamName1[] = { "temp01"};
char streamName2[] = { "temp02"};
char streamName3[] = { "temp03"};
char streamName4[] = { "temp04"};
char streamName5[] = { "temp05"};
const int temperaturePin = 0;
EthernetClient client;
M2XStreamClient m2xClient(&client, m2xKey);
#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 2
OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);
DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire);
DeviceAddress temp0 = { DS18B20のデバイスアドレス
例 0x28, 0xFF, 0xB0, 0xA5, 0x8C, 0x16, 0x03, 0x54 };
DeviceAddress temp1 = { };
DeviceAddress temp2 = { };
DeviceAddress temp3 = { };
DeviceAddress temp4 = { };
void setup() {
sensors.begin();
sensors.setResolution(TEMPERATURE_PRECISION);
Serial.begin(9600);
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip, dns_adress, gateway, subnet);
//300000ms毎に記録
MsTimer2::set(300000, timerRecord);
MsTimer2::start();
//while (!Serial) {
// ; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for Leonardo only
//}
}
void timerRecord() {
// Serial.println("Connected to Ethernet");
// printEthernetStatus();
float temp01, temp02, temp03, temp04, temp05;
sensors.requestTemperatures();
temp01 = sensors.getTempC(temp0);
temp02 = sensors.getTempC(temp1);
temp03 = sensors.getTempC(temp2);
temp04 = sensors.getTempC(temp3);
temp05 = sensors.getTempC(temp4);
// Serial.println(sensors.getTempC(temp0));
// Serial.println(sensors.getTempC(temp1));
// Serial.println(sensors.getTempC(temp2));
// Serial.println(sensors.getTempC(temp3));
// Serial.println(sensors.getTempC(temp4));
int response1 = m2xClient.updateStreamValue(deviceId, streamName1, temp01);
int response2 = m2xClient.updateStreamValue(deviceId, streamName2, temp02);
int response3 = m2xClient.updateStreamValue(deviceId, streamName3, temp03);
int response4 = m2xClient.updateStreamValue(deviceId, streamName4, temp04);
int response5 = m2xClient.updateStreamValue(deviceId, streamName5, temp05);
// Serial.print("M2x client response code: ");
// Serial.println(response);
delay(10000);
}
void printEthernetStatus() {
// print local IP
Serial.print("Local IP: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
// print subnet mask
Serial.print("Subnet Mask: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.subnetMask());
// print gateway IP
Serial.print("Gateway IP: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.gatewayIP());
// print dns IP
Serial.print("DNS IP: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.dnsServerIP());
}
void loop(){}
2019/10/9 追記:
複数(当方の場合、5つ以上)のDS20B18のコードを延長して接続するとエラー値が頻発してしまうが、これはどうも延長したり複数繋ぐとDS20B18自体が抵抗となってしまい、通常の4K7の抵抗を入れると電圧が高くなりすぎる、あるいは電流が微弱になって読み取れなくなるらしい。その場合、抵抗を低いものに変えるとうまく行く(今回は2K2の抵抗に交換)。この現象はarduinoの個体差や配置する環境によっても異なるらしく、原因がわからずに1年ぐらいトラブルシュートに時間がかかってしまった。