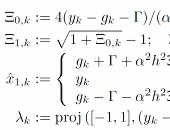Full texts are available upon request. Please email me at
-
Yachen Zhang and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Ensuring Viability: A QP-Based Inverse Kinematics for Handling Joint Range, Velocity and Acceleration Limits, as Well as Whole-body Collision Avoidance,” Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, vol.112, no. 1, p.16, March 2026.
- This paper presents a method for computing the inverse kinematics of robots under various constraints.
- Yachen Zhang's github repository
- Full text PDF (Open Access)
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1007/s10846-025-02335-z
- Springer (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a new quadratic programming (QP) based inverse kinematics (IK) method to simultaneously handle physical joint limits and whole-body collision avoidance, including self-collision and collisions with static obstacles. These constraints may conflict with each other and result in infeasible solutions of IK, which can subsequently produce unpredictable motions. The proposed method incorporates an additional linear constraint to ensure that the robot state is viable, guaranteeing the existence of solutions that do not violate the given constraints. Our IK method consists of two stages: the offline construction stage and the online computation stage. In the offline construction stage, the parameters of the proposed constraint for ensuring viable states are calculated. In the online computation stage, the proposed constraints are updated in realtime based on the robot's state, and the IK is solved as a QP problem. The proposed method can effectively handle most robots with DOFs below 10 and can also accommodate some robots with higher DOFs under simpler constraints. This marks a significant advancement compared to previous studies. The validity of the proposed method is illustrated through some simulation results.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe:“Torque-Bounded Task-Space Admittance Control for Redundant Manipulators,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 41, pp. 6642-6660, November 2025.
- It is an output of our collaboration with Kawasaki Heavy Industries.
- Youtube video
- author's version on Jxiv
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/TRO.2025.3629785
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper presents a task-space admittance controller applicable to redundant manipulators equipped with torque sensors. It extends Kikuuwe's (2019) torque-bounded admittance controller (TBAC), which allows for imposing explicit limits on the joint actuator torques without causing unsafe behaviors such as oscillation and overshoots. The proposed controller enforces that the end-effector follows predefined task-space dynamics as long as the joint torques are unsaturated and the configuration is away from singularities. The behavior in the nullspace, which arises from the redundant degrees of freedom and singular configurations, is governed by predefined joint-space dynamics. The task-space and joint-space dynamics are combined through a newly proposed continualized pseudoinverse, which employs the singular value decomposition. Results of experiments using a seven-degree-of-freedom Kinova Gen3 robot illustrate the validity of the proposed admittance controller in various scenarios, including the case where the robot is fully stretched.
|
 |
-
Yuki Yamamoto and Ryo Kikuuwe:“A Force Controller for Valve-Manipulated Hydraulic Actuators,” Control Engineering Practice, vol.156, p.106234, March 2025.
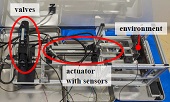
- This is an achievement of our collaboration with Kobelco Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. It proposes a new force control method for hydraulic actuators equipped with pressure sensors.
- Full text PDF (Open Access)
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1016/j.conengprac.2024.106234
- Elsevier (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
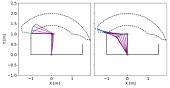
This paper proposes a force controller for hydraulic actuators of the valve-manipulated type. The structure of the proposed controller is similar to that of the admittance controllers used for robotic systems, incorporating a virtual mass-damper system that transforms the measured force to the reference velocity. In the proposed controller, the reference velocity is transformed into the valve opening commands through a quasistatic hydraulic actuator model. This paper also proposes an energy-based stabilizer that imposes limits on the reference velocity to prevent the instability induced by the deadtime, which commonly exists in hydraulic systems. The proposed controller, combined with the stabilizer, is validated with a laboratory setup composed of a linear hydraulic actuator that makes contact with a stiff external environment.
|
 |
-
Yuki Yamamoto, Jinjun Qiu, Takayuki Doi, Takao Nanjo, Koji Yamashita, and Ryo Kikuuwe:“A Position Controller for Hydraulic Excavators with Deadtime and Regenerative Pipelines,” IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, vol.22, pp.855-871, January 2025
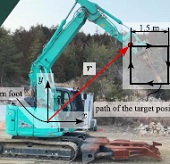
- This is an achievement of our collaboration with Kobelco Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. This paper proposes a position controller based on the hydraulic circuit model proposed in the paper 38, and applied it to a hydraulic excavator.
- Related SpeakerDeck Slides
- Full text PDF (Open Access)
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/TASE.2024.3354952
- IEEE Xplore (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a position controller for commercial hydraulic excavators. It is constructed by combining a proportional-derivative (PD) controller and a sliding-mode controller as a differential algebraic inclusion and also is integrated with a recently-proposed hydraulic actuator model. The use of the PD control is intended to make the controller insensitive to the deadtime in the hydraulic system, which is typically 0.1 s to 0.6 s in commercial excavators. The use of the sliding-mode controller combined with the actuator model is for handling the saturation of the actuator force, which may happen when the target position is not close enough to the current position and when the relief valves open. Moreover, this paper extends the controller to deal with the effect of the regenerative pipelines, which are embedded in commercial excavators to realize efficient operations but act as a source of disturbance on the controller. This paper also shows an analysis that can be used for tuning the controller parameters. The proposed controller was validated with simulations and experiments using a 13-ton class excavator, in which some set-point control tasks and trajectory-tracking tasks were performed.
|
 |
-
Ryusei Mae and Ryo Kikuuwe:“An Admittance Controller with a Jerk Limiter for Position-Controlled Robots,” Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, vol. 36, no. 2, pp.483-493, April 2024.
- This paper presents an admittance controller for position-controlled robots having significant deadtime in the dedicated controllers. We used UR3e in the velocity-command mode, which results in 6-ms deadtime from the velocity command to the response.
- Youtube Movie
- Full text PDF (Open Access)
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.20965/jrm.2024.p0483
- Fuji Technology Press (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes an admittance control scheme for robots equipped with joint-level position controllers involving deadtime. Its main feature is an elaborate discrete-time jerk limiter, which limits the third derivative of the position command sent to the controller. The jerk limiter is designed to suppress undesirable oscillation especially when the robot is in contact with stiff environments. The controller is designed as a differential inclusion involving normal cones in the continuous-time domain, and its discrete-time algorithm is derived by the implicit Euler discretization. The presented controller was validated with experiments using a collaborative robot UR3e of Universal Robots, which has the deadtime of 6 ms in the velocity-command mode.
|
 |
-
Ryo Nishimoto and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Position-Commanding Anti-Sway Controller for 2-D Overhead Cranes Under Velocity and Acceleration Constraints,” IEEE Access, vol.11, pp.35069-35079, April 2023.
- This paper proposes an anti-sway control for a crane using a simple pseudo-integrator and nonsmooth functions.
- Youtube movie
- Full text PDF (Open Access)
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3265586
- IEEE Xplore (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes an anti-sway controller for two-dimensional overhead cranes. The controller is of the position-commanding type, i.e., it sends position commands to the position-controlled trolley, and it uses the sensor information of the payload sway angle. The position commands are determined so that the trolley tracks the desired position signal sent from an upper-level controller and also so that the payload sway is damped. The sway damping is realized by a leaky integral controller, which employs a high-pass filtered time integral of the sway angle. In addition, arbitrary limits can be imposed on the first and second derivatives of the position command, and thus it is applicable to cases where the desired position signal from the upper-level controller is nonsmooth or discontinuous. Due to these features, the controller is expected to be useful in both human-operated and autonomous systems. The controller was validated with a laboratory setup. This paper also presents an algorithm that can be attached to the proposed controller to prevent the overshoot, which can take place when the desired position signal is discontinuous.
|
 |
-
Yachen Zhang and Ryo Kikuuwe: “COM Shifter and Body Rotator for Step-by-Step Teleoperation of Bipedal Robots,” IEEE Access, vol.11, pp.25786-25800, March 2023.
- This paper presents a controller to manipulate bidal robots using simple 3D pointing devices.
- Youtube movie 1
- Youtube movie 2
- Full text PDF (Open Access)
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3256720
- IEEE Xplore (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper presents a controller for step-by-step teleoperation of bipedal robots, in which the user commands the robot's foot motions in a step-by-step manner through a pair of handheld 3-dimensional pointing devices. The proposed controller is intended to allow users to precisely manipulate the swing foot motions to traverse rough terrains by avoiding obstacles. It aims to realize quick response to user commands and stable automatic balancing even under erroneous user commands. The main components of the proposed controller are a COM (center-of-mass) shifter and a body rotator, which are simple sensory feedback controllers that do not involve first-in first-output (FIFO) buffers, time-series generation, or online optimization. The COM shifter is a controller to produce a COM motion according to a reference zero moment point (ZMP). The body rotator complements the COM shifter to produce an appropriate angular momentum rate to enhance the regulation of ZMP. The proposed controller is validated in our interactive/realtime simulation environment.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Dynamics Modeling of Gear Transmissions with Asymmetric Load-Dependent Friction,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, vol.179, p.105116, January 2023.
- This paper proposes a new concise equation-of-motion representation of gear transmissions with load-depending friction, including those non-backdrivable. It can be applied to simulation of robotic systems having joints with heavy friction.
- Correction of an error: Ryo Kikuuwe:“Corrigendum to ‘Dynamics modeling of gear transmissions with asymmetric load-dependent friction’ [Mechanism and Machine Theory 179 (2023) 105116],'” Mechanism and Machine Theory, vol.186, p.105366, April 2023.
- author's final version on techRxiv
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2022.105116
- Elsevier
- [Abstract]
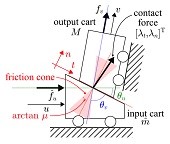
This paper proposes a new concise mathematical model of gear transmission dynamics with asymmetric load-dependent friction. It is built only upon the rigid-contact mechanics and the Coulomb friction law, but provides a new theoretical perspective on dynamic and static characteristics of gear transmissions. The presented model is of the form of a differential-algebraic inclusion (DAI) characterized by some parameters, including input-side and output-side asymmetry coefficients. The presented model properly captures the static friction and even the non-backdrivability. It is applicable to different classes of transmissions, such as leadscrew transmissions, worm gear transmissions, and spur gear transmissions. The DAI representation is extended into a multi-dimensional representation for articulated rigid-body systems driven through joint transmissions. Moreover, simulation algorithms are derived through the implicit Euler discretization. Some simulation examples illustrate the capability of the presented simulation algorithm to reproduce load-dependent asymmetric frictional behaviors, which cannot be reproduced by conventional load-independent joint friction models.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Yuki Yamamoto and Bernard Brogliato: “Implicit Implementation of Nonsmooth Controllers to Nonsmooth Actuators,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol.67, no.9, p.4645-4657, September 2022.
- This paper proposes a theoretical framework to implement a sliding mode controller to nonsmooth actuators, of which an example is hydraulic actuators detailed in the paper 38. A real-world application of the theory is reported in the paper 37.
- Full text PDF
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/TAC.2022.3163124
- IEEExplorer (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
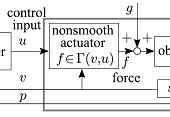
This paper presents an approach to implement a sliding-mode position controller to a plant equipped with a nonsmooth actuator. The actuator is modeled as a set-valued function from the control input and the velocity to the actuator force, which is motivated by quasistatic characteristics of hydraulic actuators shown in a previous study. The implementation of the sliding-mode controller is performed with the implicit discretization of the nominal plant model and the controller, which copes with the difficulties caused by set-valuedness, such as numerical chattering. Stability analyses both in the continuous-time and discrete-time domains are presented. Simulation results illustrate the theoretical findings.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Tomofumi Okada, Hideo Yoshihara, Takayuki Doi, Takao Nanjo and Koji Yamashita: “A Nonsmooth Quasi-Static Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Actuators,” Transactions of ASME: Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, vol.143, no.12, p.121002, December 2021.
- This is an achievement of our collaboration with Kobelco Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Full text PDF
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1115/1.4051894
- ASME Digital Library (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
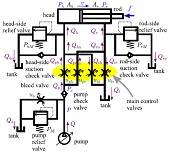
This paper presents an analytical approach for modeling the quasistatic characteristics of hydraulic actuators driven by four-valve independent metering circuits. The presented model is described as a nonsmooth, set-valued function from the velocity to the set of forces with which the equilibrium is achieved at the velocity. It is derived from algebraic relations among the velocity of the actuator, the steady-state force generated by the actuator, and the flowrate and the steady-state pressure at all valves in the circuit. This approach is also applied to more involving circuits including a regeneration pipeline and those with multiple actuators. The contribution of the paper can be seen as an example case study of the fact that these complicated circuit structures are analytically tractable through an extension of the conventional hydraulic-electric analogy. The obtained analytical expressions of the steady-state velocity-force relations allow for concise visualization of the actuators' characteristics.
|
 |
-
Yuki Yamamoto, Jinjun Qiu, Yoshiki Munemasa, Takayuki Doi, Takao Nanjo, Koji Yamashita, and Ryo Kikuuwe: “A Sliding-Mode Set-Point Position Controller for Hydraulic Excavators,” IEEE Access, vol.9, pp.153735-153749, November 2021.
- A new controller (proposed in the paper 39) based on a new physical model (proposed in the paper 38) of hydraulic actuators is applied to a hydraulic excavator. This is an outcome of our collaboration with Kobelco Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Full text PDF
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3128215
- IEEE Xplore (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a sliding-mode set-point position controller for hydraulic excavators. The controller employs a simple switching surface that exponentially drives the actuator position to the desired position with a specified time constant. The discrete-time algorithm of the controller is constructed through a double-implicit implementation scheme, which is for implementing a simple sliding-mode controller to nonsmooth actuators, including hydraulic actuators. We employ a nonsmooth quasistatic model of the hydraulic actuator, which analytically accounts for the pressure saturation caused by the relief valves and check valves and the square-root law of the pressure-flowrate relation. This paper elaborates the analytical form of the model to be combined with the double-implicit implementation. A state predictor based on the actuator model extends the controller to compensate for the deadtime in the hydraulic system. The proposed controller is validated with some simulations and also through experiments employing the swing axis of a 13-ton class excavator.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Pablo J. Prieto and J. A. López-Rentería: “Chattering of Proxy-based Sliding Mode Control in the Presence of Parasitic Dynamics,” IMA Journal of Mathematical Control and Information, vol.38, no.1, pp.177-191, March 2021.
- This paper applies the describing function method to PSMC. It is a joint work with Dr. Prieto (CETYS Universidad, Tijuana, Mexico), who is a user of PSMC.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1093/imamci/dnaa006
- Oxford Academic
- [Abstract]
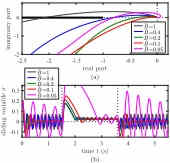
This paper reports an analysis on proxy-based sliding mode control (PSMC), which is a controller proposed by Kikuuwe and Fujimoto (2006) originally for position control of robot manipulators. The describing function method is employed to investigate the chattering behavior of PSMC combined with a simple second-order plant with parasitic dynamics. The results show that PSMC is capable of achieving a lower tendency to chattering than the boundary-layer implementation of sliding mode control with the same sliding surface, without affecting the insensitivity to disturbance.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Sliding Motion Accuracy of Proxy-Based Sliding Mode Control Subjected to Measurement Noise and Disturbance,” European Journal of Control, vol.58, pp.114-122, March 2021.
- SpeakerDeck Slides of a preliminary version.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1016/j.ejcon.2020.07.005
- Elsevier
- [Abstract]
The proxy-based sliding mode control (PSMC) is a previously-proposed controller for the position control of robotic manipulators. It is an alternative approximation of a simple sliding mode control (SMC) of which the set-valuedness is relaxed in a particular differential-algebraic manner, and has been found useful for many applications especially in robotics. This paper presents the results of frequency-domain analysis and simulations to clarify the mathematical nature of PSMC subjected to measurement noise and disturbance. The results show that, in the presence of measurement noise and disturbance, the sliding motion realized by PSMC is closer to that of the ideal SMC than those of conventional implementations of SMC with the boundary-layer approximation and low-pass filtering. Comparisons in terms of the chattering intensity and the sliding motion accuracy are also presented. Moreover, it is shown that PSMC's response to disturbance in the sliding motion is quite different from that of the conventional implementations.
|
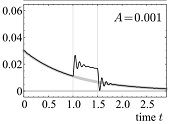 |
-
Gyuho Byun and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Improved Sliding Mode Differentiator Combined with Sliding Mode Filter for Estimating First and Second-Order Derivatives of Noisy Signals,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, vol.18, no.12, pp.3001-3014, December 2020.
|
 |
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe, Shyam Kamal and Shanhai Jin: “Implicit-Euler Implementation of Super-Twisting Observer and Twisting Controller for Second-Order Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol.67, no.11, pp.2607-2611, November 2020.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/TCSII.2019.2957271
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes new discrete-time algorithms of the super-twisting observer and the twisting controller to be applied to second-order systems. The algorithms are based on the full implicit-Euler discretization, which contributes to the elimination of chattering. Proofs of some stability properties of the discretized twisting controller are also provided. Simulations show that, as compared to traditional explicit-Euler schemes, the proposed scheme avoids the chattering both in trajectory tracking output and control input in the presence of external disturbances.
|
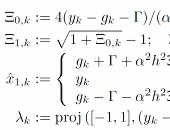 |
-
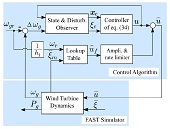
Nehal Baiomy and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Amplitude- and Rate-Saturated Collective Pitch Controller for Wind Turbine Systems,” Renewable Energy, vol.158, pp.400-409, October 2020.
- This paper presents an application of the control technique presented in the paper 30 below to wind turbine systems. The technique is tested with simulation using FAST.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.112
- Elsevier
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a new collective pitch controller for wind turbine systems to maintain the generator speed constant at the rated value in the region above the rated wind speed. It provides the command of the collective pitch angle to the wind turbine system, and one can impose explicit limits on the magnitude and the rate-of-change of the pitch angle command. In addition, the controller involves a variable gain that realizes non-overshooting convergence from the large errors in the generator speed and accurate regulation of the generator speed near the rated value. This controller is an extension of an amplitude- and ratesaturated controller previously proposed by the authors. It is combined with a state and disturbance observer and a lookup table-based feedforward. The proposed controller is validated through a software simulator FAST emulating a three-bladed horizontal-axis wind turbine system.
|
 |
-
Gyuho Byun and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Stiff and Safe Task-Space Position and Attitude Controller for Robotic Manipulators,” ROBOMECH Journal, vol.7, article 18, March 2020.
- DOI:10.1186/s40648-020-00166-1
- Springer (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
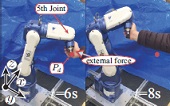
This paper proposes a stiff and safe task-space position and attitude control scheme for robotic manipulators. This study extends the work of Kikuuwe et al’s. (2006) velocity-bounding proxy-based sliding mode control by explicitly addressing the attitude part. The proposed controller has a Jacobian-based structure, which realizes smooth trajectories when the desired attitude is far rotated from the actual attitude. It also imposes arbitrary magnitude limits on the end-effector velocity, angular velocity, and each actuator force without sacrificing a stiffness, which is the same level as a high-gain PID position control below the limits. The benefit of the proposed controller becomes apparent after the robot yields to external forces due to force saturations, when the robot makes contact with obstacles. In such a situation, if the external forces disappear, the controller generates overdamped resuming motion from large tracking errors. The proposed controller can be expected to enhance the safety of robotic applications for the human-robot interaction. The proposed method is validated by experiments employing a six-degree of freedom industrial manipulator.
|
 |
-
Nehal Baiomy and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Amplitude- and Rate-Saturated Controller for Linear Plants,” Asian Journal of Control, Vol.22, No.1, pp.77-91, January 2020.
- A parameter tuning guideline for this controller is published in the paper 27 below, which was submitted after this paper.
- Full text PDF made available by Wiley's OnlineOpen option
- DOI:10.1002/asjc.1851
- Wiley (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
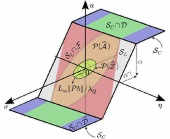
This paper proposes a new nonlinear controller applicable to single-input linear systems under bounded disturbance. The controller provides control signals satisfying specified amplitude and rate-of-change limitations. This feature is realized by its sliding mode-like structure comprising a set-valued function. The controller also employs a state-dependent parameter to broaden the region of attraction and to shrink the terminal attractor. In addition, this paper provides a discrete-time implementation of the proposed controller based on a model-based implicit discretization scheme. Numerical examples show the validity of the proposed controller.
|
 |
-
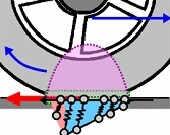
Ryo Kikuuwe: “A Brush-Type Tire Model with Nonsmooth Representation,” Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Vol.2019, Article 9747605, December 2019.
- This paper also includes a dissipation potential function to produce the friction force with two-dimensional (multidimensional) Stribeck effect.
- SpeakerDeck Slides of a preliminary version presented at an Euromech Colloquium. It is slightly different from this paper's content.
- Youtube movie
- Full text PDF
- DOI:10.1155/2019/9747605
- Hindawi (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a brush-type tire model with a new mathematical representation. The presented model can be seen as a generic model that describes the distributed viscoelastic force and Coulomb-like friction force, which are balancing each other at each point, in the contact patch. The model is described as a partial differential algebraic inclusion (PDAI), which involves the set-valuedness to represent the static friction. A numerical integration algorithm for this PDAI is derived through the implicit Euler discretization along both space and time. Some numerical
comparisons with Magic Formula and a LuGre-based tire model are presented. The results show that, with appropriate choice of parameters, the proposed model is capable of producing steady-state characteristics similar to those of Magic Formula. It is also shown that the proposed model realizes a proper static friction state, which is not realized with a LuGre-based tire model.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Torque-Bounded Admittance Control Realized by a Set-Valued Algebraic Feedback,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, Vol.35, No.5, pp.1136-1149, October 2019.
- SpeakerDeck Slides
- Youtube movies: movie1, movie2.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the author's version
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1109/TRO.2019.2920069
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a new admittance controller that realizes safe behavior even under torque saturation. The new controller is analytically equivalent to a conventional admittance controller as long as the actuator torque is not saturated, but is free from unsafe behaviors such as snapping-back, oscillation, or overshoots, which may happen with conventional admittance controllers after torque saturation. The new controller is described by a differential algebraic inclusion, and can be understood as a conventional admittance controller expanded with an additional algebraic loop through a normal-cone operator. Its continuous-time representation involves a nonsmooth, set-valued function, but its discrete-time implementation is free from set-valuedness and given as a closed-form algorithm as a result of the use of implicit (backward) Euler discretization. The controller was tested with one joint of an industrial manipulator equipped with a force sensor.
|
 |
-
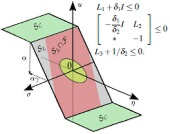
Nehal Baiomy and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Parameter Selection Procedure for an Amplitude- and Rate-Saturated Controller,” International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems,, Vol.17, No.4, pp.926-935, April 2019.
|
 |
-
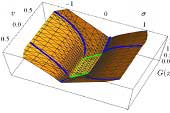
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Some Stability Proofs on Proxy-Based Sliding Mode Control,” IMA Journal of Mathematical Control and Information, Vol.35, No.4, pp.1319-1341, December 2018.
- Full text PDF
This file has been posted here in accordance with the publisher's self-archiving policy instructed here.
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1093/imamci/dnx030
- Oxford Academic (free-access article link)
- Oxford Academic
- [Abstract]
Proxy-based sliding mode control (PSMC) is a control scheme proposed a decade ago originally as a position controller for robot manipulators. This controller has a unique mathematical structure that combines a PID controller and a sliding mode controller in an algebraic way, and has demonstrated its practical usefulness in various applications. Its theoretical foundation, however, has been quite immature. This paper presents a set of stability proofs on PSMC as a minimum requirement for future practical applications. Finite-time stability and asymptotic stability of terminal attractors are proven with the use of a nonsmooth Lyapunov function.
|
 |
-
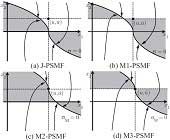
Myo Thant Sin Aung, Zhan Shi and Ryo Kikuuwe: “A New Parabolic Sliding Mode Filter Augmented by a Linear Low-Pass Filter and Its Application to Position Control,” Transactions of ASME: Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, Vol.140, No.4, Article 041005, April 2018.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- ASME Digital Library
- DOI:10.1115/1.4037732
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a new sliding mode filter augmented by a linear low-pass filter for mitigating the effect of high frequency noise. It is based on the derivation of three new variants of Jin et al.’s (2012) parabolic sliding mode filter (J-PSMF) and investigation on their frequency-response characteristics. The new filter is developed by augmenting one of the variants of J-PSMF by a second order linear low-pass filter. It has better balance between the noise attenuation and signal preservation than both linear lowpass filters and J-PSMF. The effectiveness of the new filter is experimentally evaluated on a DC servo motor equipped with an optical encoder. This paper also shows the application of the proposed filter to a positioning system under PDD2 (proportional, derivative, and second derivative) control, which successfully realizes the noise attenuation and the non-overshooting response simultaneously.
|
 |
-
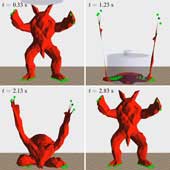
Ryo Kikuuwe: “A Time-Integration Method for Stable Simulation of Extremely Deformable Hyperelastic Objects,” The Visual Computer, Vol.33, No.10, pp.1335-1346, October 2017.
- YouTube movie
- Full text will be available upon request.
- Full text of a view-only version under "SharedIt" initiative
- PDF of the author's version
- ResearchGate
- Springer
- DOI:10.1007/s00371-016-1225-0
- [Abstract]
This paper presents a time integration method for realtime simulation of extremely deformable objects subject to geometrically nonlinear hyperelasticity. In the presented method, the equation of motion of the system is discretized by the backward Euler method, and linearly approximated through the first-order Taylor expansion. The approximate linear equation is solved with Quasi-Minimal Residual method (QMR), which is an iterative linear equation solver for non-symmetric or indefinite matrices. The solution is then corrected considering the nonlinear term that is omitted at the Taylor expansion. The method does not demand the constitutive law to guarantee the positive definite of the stiffness matrix. Experimental results show that the presented method realizes stable behavior of the simulated model under such deformation that the tetrahedral elements are almost flattened. It is also shown that QMR outperforms Biconjugate Gradient Stabilized method (BiCGStab) in this application.
|
 |
-
Myo Thant Sin Aung and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Stability Enhancement of Admittance Control with Acceleration Feedback and Friction Compensation,” Mechatronics, Vol.45, pp.110-118, August 2017.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
- ResearchGate
- Elsevier
- DOI:10.1016/j.mechatronics.2017.06.011
- [Abstract]
This paper presents an experimental investigation of a new position control scheme that enhances the stability of admittance control by using: (a) PDD2 (proportional, derivative, and second derivative) feedback, (b) dither-based friction compensation and (c) sliding-mode-based noise filter with a variable gain. The PDD2 structure and the friction compensation are for expanding the bandwidth of the internal position-controlled subsystem. The sliding-mode-based filter is for the attenuation of noise in the acceleration signal without producing a large phase lag. The variable gain of the filter is for suppressing acceleration measurement noise at low velocity. The proposed controller is validated by employing a 1-DOF device.
|
 |
-
Masayoshi Iwatani and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Some Improvements in Elastoplastic Friction Compensator,” SICE Journal of Control, Measurement, and System Integration, Vol.10, No.3, pp.141-148, May 2017.
- Full text PDF.
- DOI:10.9746/jcmsi.10.141
- J-Stage (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
For robotic joints with compliant transmissions, Mahvash and Okamura have proposed a friction compensator based on an elastoplastic friction model. One drawback of the compensator is that the compensator continues producing non-zero output force in the static friction state, which results in the degraded backdrivability of joints. In order to remedy this problem, this paper proposes an elastoplastic friction compensator with improved static friction behavior, which is realized by an additional term that makes the output force exponentially decay in the static friction state. This paper also proposes an additional algorithm that adjust the decay rate of the output force in real time. The proposed methods are experimentally tested with a linear actuator with a timing belt and a six-axis industrial manipulator.
|
 |
-
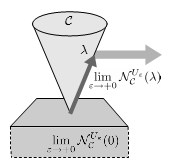
Ryo Kikuuwe and Bernard Brogliato: “A New Representation of Systems with Frictional Unilateral Constraints and Its Baumgarte-Like Relaxation,” Multibody System Dynamics, Vol.39, No.3, pp.267-290, March 2017.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- Full text of a view-only version under "SharedIt" initiative
- PDF of the authors' version
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1007/s11044-015-9491-6
- Springer
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a new representation of multibody mechanical systems involving three-dimensional frictional unilateral constraints. The new representation is of the form of a differential algebraic inclusion (DAI) employing a normal cone with a non-Euclidean, singular norm metric. It can be seen as a generalization of a differential algebraic equation (DAE) using Lagrange multipliers, which has been used to represent mechanical systems with equality constraints. The paper also presents an approach to approximate the aforementioned DAI by another form of DAI, which can be equivalently converted into an ordinary differential equation (ODE). The approach can be seen as a generalization of the Baumgarte stabilization, which is originally for DAEs. The new DAI representation and its ODE approximation are illustrated with some simple examples.
|
 |
-
Masayoshi Iwatani and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Identification Procedure for Rate-Dependency of Friction in Robotic Joints with Limited Motion Ranges,” Mechatronics, Vol.36, pp.36-44, June 2016.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
- ResearchGate
- Elsevier
- [Abstract]
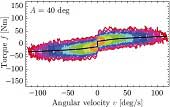
This paper proposes a procedure for identifying rate-dependent friction of robotic manipulators of which the motion is limited due to the configuration or the environment. The procedure is characterized by the following three features: (i) the rate dependency is represented by line sections connecting sampled velocityforce pairs, (ii) the robot is position-controlled to track desired trajectories that are some cycles of sinusoidal motion with different frequencies, and (iii) each velocity-force pair is sampled from one cycle of the motion with subtracting the effects of the gravity and the inertia. The procedure was validated with a six axis industrial robotic manipulator YASKAWA MOTOMAN-HP3J, of which the joints are equipped with harmonic-drive transmissions of the reduction ratios of 81.5 to 224. The experimental results show that the identification is achieved with a sufficient accuracy with the 20 degrees of motion of each joint. In addition, the results were utilized for friction compensation, successfully reducing the effect of the friction by 60 to 80 percent.
|
 |
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Implicit Euler Simulation of One-Dimensional Burridge-Knopoff Model of Earthquakes with Set-Valued Friction Laws,” Advances in Computational Mathematics, Vol.41, No.6, pp.1039-1057, December 2015.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- Springer
- [Abstract]
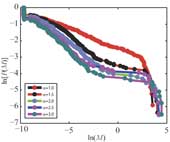
In the simulations of Burridge-Knopoff (BK) model of earthquakes, the friction force laws are important to produce earthquake-like stick-slip behaviors. Some friction force laws are set-valued and the BK model with them can produce consistent results with observed data of earthquakes in some aspects. However, it is cumbersome to simulate the BK model with set-valued laws by conventional explicit integration methods. In the presence of set-valued laws, the explicit integration methods can easily lead to the numerical chat-tering, violated constraints on the velocity of force laws, and the difficulty of identifying the states of blocks of the BK model. This paper employs an implicit Euler integration method to simulate the BK model with symmetric and asymmetric set-valued laws. This method removes the numerical chattering in the BK model, even in the cases of large time step sizes. It can easily detect the stuck or slipping state of a block element. Comparing to previous results integrated by explicit integration methods in the literature, the results integrated by this implicit method show smoother curves and lower irregularities in the magnitude distribution of events.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Katsuya Kanaoka, Tomohiro Kumon and Motoji Yamamoto: “Phase-Lead Stabilization of Force-Projecting Master-Slave Systems with a New Sliding Mode Filter,” IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, Vol.23, No.6, pp.2182-2194, October 2015.
- YouTube movies: movie1, movie2
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
- ResearchGate
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
Force-projecting master-slave control scheme is the reversed implementation of the conventional force-reflecting scheme. This paper presents a method to stabilize force-projecting master-slave systems by using the linear phase-lead compensator and a new nonlinear filter. The nonlinear filter is a modified version of Jin et al.'s (2012) parabolic sliding mode filter, which produces relatively small phase lag. Some numerical properties of the new filter are presented. The filter is then applied to an experimental master-slave system composed of two industrial manipulators. The force scaling factor of 25 was achieved with maintaining the stability.
|
 |
-
Myo Thant Sin Aung, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Friction Compensation of Geared Actuators with High Presliding Stiffness,” Transactions of ASME: Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, Vol.137, No.1, Article 011007, January 2015.
- YouTube movie
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- ASME Digital Library
- [Abstract]
Most of existing friction compensation techniques are based on friction models that uses the velocity as its input. These methods are difficult to apply to inexpensive encoderbased actuator systems that do not exhibit sufficiently large presliding displacement. This paper presents a new method of friction compensation that can be applied to geared actuators with high presliding stiffness. The compensator consists of three components that compensate (a) static friction, (b) rate-dependent kinetic friction, and (c) dynamic friction involving presliding viscoelasticity. The first component employs dither-like torque command, and the other two are based on friction models involving pre-calibrated parameters. The proposed method is validated through experiments employing a harmonic drive transmission. In particular, it is suggested that the dither-like static friction compensation and the viscosity in the presliding model significantly improve the performance of the compensator.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe: “A Sliding-Mode-Like Position Controller for Admittance Control with Bounded Actuator Force,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, Vol.19, No.5, pp.1489-1500, October 2014.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the author's version
©IEEE, 2013. This is the author's version of an article that has been published in this journal. It is posted here by permission of IEEE for your personal use. Not for redistribution. Changes were made to this version by the publisher prior to publication. The final version of record is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2013.2286411.
- ResearchGate
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a new position controller that is suitable for the use as the internal position servo of an admittance controller with bounded actuator forces. The new position controller approximately behaves as a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller with an acceleration feedforward in normal situations and as a sliding mode controller when the actuator force is saturated. The admittance controller employing the new position controller realizes smooth transitions between saturated periods and unsaturated periods. Moreover, it quickly responds to changes in the applied force even when the actuator force is saturated, leading to better stability and smoothness. The controller was validated through experiments using a robotic manipulator.
|
 |
-
Shanhai Jin, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Improving Velocity Feedback for Position Control by Using a Discrete-Time Sliding Mode Filtering with Adaptive Windowing,” Advanced Robotics, Vol.28, No.14, pp.943-953, July 2014.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- Taylor & Francis Group
- [Abstract]
In position control of mechatronic devices, velocity feedback is important for injecting additional damping to avoid low-frequency fluctuation around desired trajectories. In practice, velocity signal is often obtained by finite difference of position signal from an optical encoder. However, such a numerical differentiation produces high-frequency noise by magnifying quantization error contained in the position signal. As a result, the controller may produce high-frequency vibration. This paper presents a new noise-reduction discrete-time filter based on sliding mode and adaptive windowing. The presented filter is an improved version of a sliding mode filter by Jin et al. (2012), with including adaptive windowing of which the window size is determined in a similar way to that of a discrete-time adaptive windowing differentiator by Janabi-Sharifi et al.(2000). The presented filter is then applied to a position control of a mechatronic device for improving velocity feedback. Experimental results show that the presented filter provides better velocity feedback than its previous version, Janabi-Sharifi et al.'s differentiator, and combinations of these two filters.
|
 |
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “A Contact Force Model with Nonlinear Compliance and Residual Indentation,” Transactions of ASME: Journal of Applied Mechanics, Vol.81, No.2, Article 021003, February 2014.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- ASME Digital Library
- [Abstract]
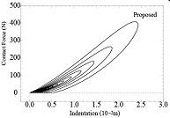
The contact between two bodies is a complicated phenomenon in which the force and the relative position have nonlinear relations. Empirical results in the literature show that, in some mechanical systems such as biological tissues, the relation between the contact force and the indentation is characterized by the following three features: (i) continuity of the force at the time of collision, (ii) a Hertz-like nonlinear force-indentation curve, and (iii) nonzero indentation at the time of loss of contact force. The conventional Hunt-Crossley (HC) model does not capture the feature (iii) as the model makes the contact force and the indentation reach zero simultaneously. This paper proposes a compliant contact model based on a differential-algebraic equation that satisfies all three features. The behaviors of the model and the effect of the parameters in the model are investigated through numerical simulations.
|
 |
-
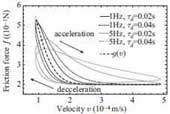
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “A Multistate Friction Model Described by Continuous Differential Equations,” Tribology Letters, Vol.51, No.3, pp.513-523, September 2013.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.1007/s11249-013-0187-x
- Springer
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a multistate friction model derived from a set of differential-algebraic inclusions (DAIs). This model is described as a set of continuous differential equations that describe both the presliding and sliding regimes in a unified expression. It reproduces major features of friction phenomena reported in the literature, such as the Stribeck effect, nondrifting property, stick-slip oscillation, presliding hysteresis with nonlocal memory, and frictional lag. Moreover, the new model does not produce unbounded positional drift or non-smooth forces, which are major problems of previous models due to the mathematical difficulty in dealing with transitions between the presliding and sliding regimes. The model is validated through comparison between its simulation results and empirical results in the literature.
|
 |
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “A Differential-Algebraic Method to Approximate Nonsmooth Mechanical Systems by Ordinary Differential Equations,” Journal of Applied Mathematics, Vol.2013, Article 320276, May 2013.
- [YouTube]
- Full text PDF
- DOI:10.1155/2013/320276
- Springer (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
Nonsmooth mechanical systems, which are mechanical systems involving dry friction and rigid unilateral contact, are usually described as differential inclusions (DIs), i.e., differential equations involving discontinuities. Those DIs may be approximated by ordinary differential equations (ODEs) by simply smoothing the discontinuities. Such approximations, however, can produce unrealistic behaviors because the discontinuous natures of the original DIs are lost. This paper presents a new algebraic procedure to approximate DIs describing nonsmooth mechanical systems by ODEs with preserving the discontinuities. The procedure is based on the fact that the DIs can be approximated by differential algebraic inclusions (DAIs) and thus they can be equivalently rewritten as ODEs. The procedure is illustrated by some examples of nonsmooth mechanical systems with simulation results obtained by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method.
|
 |
-
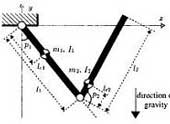
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Alternative Proofs of Four Stability Properties of Rigid Link Manipulators under PID Position Control,” Robotica, Vol.31, No.1, pp.113-122, January 2013.
- Full text PDF
©2012 Cambridge University Press. This file has been posted here in accordance with the publisher's copyright policy instructed here.
- ResearchGate
- Cambridge Journal Online
- [Abstract]
This paper presents new proofs of four stability properties (semiglobal strict passivity, semiglobal asymptotic stability, semiglobal input-to-state stability, and semiglobal uniform ultimate boundedness with an arbitrarily reducible ultimate bound) of a rigid-link manipulator under proportional-integral-derivative (PID) position control. The proofs employ a strict Lyapunov function and a novel parameterization to provide four inequality conditions for the stability properties. In those inequalities, arithmetic operations on physical quantities are physically consistent if the joints are all revolute or all prismatic. A gain selection procedure is presented by which the ultimate bounds of velocity error, position error, and its integral can be independently designed.
|
 |
-
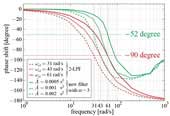
Shanhai Jin, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Parameter Selection Guidelines for a Parabolic Sliding Mode Filter Based on Frequency and Time Domain Characteristics,” Journal of Control Science and Engineering, Vol.2012, Article 923679, December 2012.
- Full text PDF
- Hindawi (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
In a previous paper, the authors proposed a new parabolic sliding mode filter for removing noise from signals in robotics and mechatronics applications. This paper presents the results of quantitative performance evaluation of the filter based on the frequency and time domain characteristics, and presents selecting guidelines of two parameters of the filter based on the evaluation results. It is shown that, in the frequency domain, the noise removing capability of the filter is almost the same as that of the second-order Butterworth low-pass filter (2-LPF), but its phase lag is smaller (maximum 150 degree) than that of 2-LPF (maximum 180 degree). Moreover, the filter produces smaller phase lag than a conventional sliding mode filter proposed by Han andWang (1994) and Emaru and Tsuchiya (2000) with appropriate selection of the parameters. It is also shown that, in the time domain, the filter produces smaller overshoot than 2-LPF and the conventional one, while maintaining short transient time, by using an appropriately selected parameter. The presented parameter selection guidelines state that the values of the parameters should be chosen according to some estimated characteristics of the input and some desired characteristics of the output. The validity of the filter and the presented guidelines is validated through numerical examples. In addition, the filter was implemented to a closed-loop, force control system comprising a robot manipulator, and the experimental results show the effectiveness of the filter and the presented guidelines.
|
 |
-
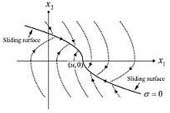
Shanhai Jin, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Real-Time Quadratic Sliding Mode Filter for Removing Noise,” Advanced Robotics, Vol.26, No.8-9, pp.877-896, July 2012.
- [Abstract]
This paper presents a sliding mode filter for removing noise. It effectively removes impulsive noise and highfrequency noise, producing a smaller phase lag than linear filters. In addition, it is less prone to overshoot than previous sliding mode filters and it does not produce chattering. It is computationally inexpensive and thus suitable for real-time applications. The proposed sliding mode filter employs a quadratic surface as its sliding surface, which is designed so that the output converges to the input in finite time when the input value is constant. Its algorithm is derived by using the backward Euler discretization, which can be used to prevent chattering. The effectiveness of the filter was shown by experiments using an ultrasonic sensor and an optical encoder.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Kenta Nakamura and Motoji Yamamoto: “Finger-Mounted Tactile Sensor for Evaluating Surfaces,” Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol.24, No.3, pp.430-440, June 2012.
- This is a translated paper. The original version (in Japanese) is found here.
- ResearchGate
- DOI:10.20965/jrm.2012.p0430
- Fuji Technology Press (Open Access)
- [Abstract]
This paper presents a finger-mounted tactile sensor for extracting information on fine surface properties of objects such as textile fabrics. The prototype sensor has a thin structure composed of a sheet of PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) film sensor and some metal parts for converting compressive forces into area expansion of the PVDF film. By using a signal processing program based on the FFT (fast Fourier transform), voltage signal sequences from nine different fabrics were distinguished, even in the presence of variations in the pressing force and the speed of rubbing motion induced by the fluctuations in the user's hand motion. In addition, the signal sequences from abraded fabrics were sorted by their levels of abrasion by extracting a signal component correlated with the abrasion level.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Satoshi Yasukouchi, Hideo Fujimoto and Motoji Yamamoto: “Proxy-Based Sliding Mode Control: A Safer Extension of PID Position Control,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, Vol.26, No.4, pp.670-683, August 2010.
- What is Proxy-Based Sliding Mode Control?
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work. Copyright and all rights therein are retained by authors or by other copyright holders. All persons copying this information are expected to adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author's copyright. In most cases, these works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.
- [IEEE Copyright Policy (Section 8.1.9 of IEEE PSPB Operations Manual)]
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
High-gain proportional-integral-derivative (PID) position control involves some risk of unsafe behaviors in cases of abnormal events, such as unexpected environment contacts and temporary power failures. This paper proposes a new position-control method that is as accurate as conventional PID control during normal operation, but is capable of slow, overdamped resuming motion without overshoots from large positional errors that result in actuator-force saturation. The proposed method, which we call proxy-based sliding mode control (PSMC), is an alternative approximation of a simplest type of sliding mode control (SMC), and also is an extension of the PID control. The validity of the proposed method is demonstrated through stability analysis and experimental results.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Hiroaki Tabuchi and Motoji Yamamoto: “An Edge-Based Computationally Efficient Formulation of Saint Venant-Kirchhoff Tetrahedral Finite Elements,” ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol.28, No.1, pp.8:1-8:13, January 2009.
-
[Movie 1]
[Movie 2]
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
- ResearchGate
- ACM Digital Library
©ACM, 2009. This is the author's version of the work. It is posted here by permission of ACM for your personal use. Not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, Volume 28, Issue 1 (January 2009) http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1477926.1477934
- [Abstract]
This article describes a computationally efficient formulation and an algorithm for tetrahedral finite-element simulation of elastic objects subject to Saint Venant-Kirchhoff (StVK) material law. The number of floating point operations required by the algorithm is in the range of 15% to 27% for computing the vertex forces from a given set of vertex positions, and 27% to 38% for the tangent stiffness matrix, in comparison to a well-optimized algorithm directly derived from the conventional Total Lagrangian formulation. In the new algorithm, the data is associated with edges and tetrahedron-sharing edge-pairs (TSEPs), as opposed to tetrahedra, to avoid redundant computation. Another characteristic of the presented formulation is that it reduces to that of a spring-network model by simply ignoring all the TSEPs. The technique is demonstrated through an interactive application involving haptic interaction, being combined with a linearized implicit integration technique employing a preconditioned conjugate gradient method.
- This paper was presented at SIGGRAPH 2009.
- The travel expense for attending SIGGRAPH 2009 was partially supported by The Murata Science Foundation.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Naoyuki Takesue and Hideo Fujimoto: “A Control Framework to Generate Nonenergy-Storing Virtual Fixtures: Use of Simulated Plasticity,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, Vol.24, No.4, pp.781-793, August 2008.
- PDF file
©2008 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
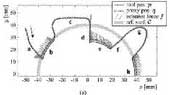
Some recent studies have addressed a class of human-machine coordination employing "virtual fixtures," which are computer-generated walls or guides presented through haptic devices for assisting precise path tracing and for preventing the entry to specified regions. This paper presents the concept and control algorithms of a new class of virtual fixtures that is based on simulated plasticity. The plasticity-based virtual fixtures act as hard walls as long as the user's force is smaller than a predetermined yield force, but the user can deviate from the fixtures by intentionally producing a force larger than the yield force. As a characteristic of plasticity, the proposed virtual fixtures do not store elastic energy; the reaction force from the fixture almost always opposes the user's motion to decelerate the motion. Thus, the plasticity-based virtual fixtures are expected to be useful in some applications where safety is an utmost priority. This paper presents control algorithms for realizing the concept of plasticity-based virtual fixtures, addressing technical challenges in treating discontinuous nature of plasticity in discrete-time systems. The algorithms were demonstrated through experiments using impedance-type and admittance-type haptic devices.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Takahiro Yamamoto and Hideo Fujimoto: “A Guideline for Low-Force Robotic Guidance for Enhancing Human Performance of Positioning and Trajectory Tracking: It Should Be Stiff and Appropriately Slow,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part A: Systems and Humans, Vol.38, No.4, pp.945-957, July 2008.
- How slow should a robot be?: Physics of human-robot coordination.
- PDF file
©2008 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper considers the application of a low-force robotic manipulator to guide a human user's movements to place a tool (or the user's hand) at a predetermined position or move it along a predetermined trajectory. This application is potentially useful, e.g., skill training for humans, rehabilitation, and human-machine coordination in the manufacturing industry. A proportional-derivative (PD)-type position control can be used for this application, but the parameters for the controller should be appropriately chosen for enhancing the human performance of positioning and trajectory tracking. We hypothesize that the robot's position control should be stiff and appropriately slow, i.e., the proportional gain should be high and the time constant (the ratio of the derivative gain to the proportional gain) should be appropriately large. Such characteristic has been difficult to be realized in ordinary PD position control because it requires direct high-gain velocity feedback. However, our recent technique, which is proxy-based sliding mode control (PSMC), is capable of producing such a hypothetically preferred response and allows us to empirically validate the hypothesis. The results of experiments using two distinctly different robotic devices supported the hypothesis, showing that the time constant should be set around 0.1 s rather than 0.01 and 0.5 s.
|
 |
-
Naoyuki Takesue, Akihito Sano, Hiromi Mochiyama, Ryo Kikuuwe, Taiki Ishiguro and Hideo Fujimoto: “Analysis and Experiment of Helical Spring-Type Pressure and Shear Sensor,” Journal of System Design and Dynamics, Vol.1, No.3, pp.629-637, August 2007.
- Full text PDF
- This is a translated paper. The original version (in Japanese) is found here.
- J-Stage
- [Abstract]
In this paper, we propose a sensor that detects both pressure and shear information by a helical spring and strain gages. The stresses working on the wire of spring are analyzed. The guideline to attach strain gages on the spring is discussed and the calibration procedure is shown. Finally, experiments are carried out and the effectiveness of the sensor is shown.
|
 |
- Ryo Kikuuwe, Naoyuki Takesue, Akihito Sano, Hiromi Mochiyama and Hideo Fujimoto: “Admittance and Impedance Representations of Friction Based on Implicit Euler Integration,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, Vol.22, No.6, pp.1176-1188, December 2006.
- PDF file
©2006 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
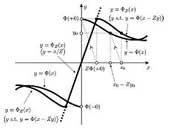
Modeling of friction force is cumbersome because of its discontinuity at zero velocity. This paper presents a set of discrete-time friction models for the purpose of haptic rendering and virtual environment construction. These models allow friction to be treated as an admittance-type or impedance-type element of a virtual environment. They are derived from implicit Euler integration of Coulomb-like discontinuous friction and linear mass-spring-damper dynamics, and have closed-form expressions. They include rate-dependent friction laws, and their extension to multidimensional cases is easy in most practical cases. The validity of the models is demonstrated through numerical examples and implementation experiments.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Tsuneo Yoshikawa: “Recognizing Object Surface Properties Using Impedance Perception,” Robotica, Vol.23, No.3, pp.387-396, May 2005.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- Cambridge University Press
- [Abstract]
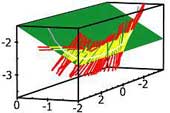
By using the impedance perception algorithm, which we previously proposed, the stiffness matrix that constrains the motion-force relation of a robot's end-effector is calculated in real-time. In this paper, we describe methods of extracting information concerning certain local properties of object surfaces from the stiffness matrix when the end-effector is slid on the surfaces. We develop two algorithms to deal with two classes of surfaces: flat and convex cylindrical surfaces. Since the proposed methods are designed separately from control strategies, they can be used for both autonomous and remote controlled robots. The results of preliminary experiments are presented.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Tsuneo Yoshikawa: “Robot Perception of Impedance,” Journal of Robotic Systems, Vol.22, No.5, pp.231-247, May 2005.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- ResearchGate
- Wiley InterScience
- DOI:10.1002/rob.20062
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes an algorithm for robot perception of impedance, which can be used as a fundamental technique for real-time and qualitative perception of physical constraints imposed on the robot's end-effector. This algorithm (1) estimates the impedance that represents the motion-force relation of the end-effector; (2) calculates the uncertainties of the estimates; and (3) detects discontinuous changes in the impedance. The estimated impedance can be used to recognize local dynamic properties of the environment and temporary constraint conditions imposed on the end-effector. The detected discontinuities can be used to segment the manipulated tasks and to recognize the geometric structure of the environment. This method can be implemented in both autonomous and remote-controlled robots because it is designed separately from control methodologies. Results of preliminary experiments are presented.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Akihito Sano, Hiromi Mochiyama, Naoyuki Takesue and Hideo Fujimoto: “Enhancing Haptic Detection of Surface Undulation,” ACM Transactions on Applied Perception, Vol.2, No.1, pp.46-67, January 2005.
- This paper presents a "Tactile Contact Lens," which is a simple monolithic device to enhance the human tactile sense in a particular way. We got some awards for this invention.
- Full text will be available upon request.
- PDF of the authors' version
©ACM, 2004. This is the author's version of the work. It is posted here by permission of ACM for your personal use. Not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in ACM Transactions on Applied Perception, Volume 2, Issue 1 (January 2005) http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1048687.1048691
- ACM Digital Library
- [Abstract]
This paper introduces a device for enhancing detection of surface undulation through active touch. This device, which we call a "tactile contact lens," is composed of a sheet and numerous pins arranged on one side of the sheet. Experimental results show that a small bump on a surface can be detected more accurately through this device than by bare finger and than through a flat sheet. A mathematical analysis of this phenomenon suggests two possible explanations for this phenomenon. One lies in the lever-like behavior of the pins. The pins convert the local inclination of the object surface into the tangential displacement of the skin surface. The second is the spatial aliasing effect resulting from the discrete contact. Due to this effect, the temporal change in the skin surface displacement is efficiently transduced into the temporal change in the skin tissue strain. The results of this analysis are then discussed in relation to other sensitivity-enhancing materials, tactile sensing mechanisms, and tactile/haptic display devices.
|
 |
-
Kenshiro Yamashita and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Trajectory Generation for Tip-Over Prevention and Collision Avoidance of Automatic Excavators,” Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2026), pp. 1451-1456, January 2026 (Cancun, Mexico).
-
Kohki Yamamoto and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Position and Attitude Estimation for Hydraulic Excavator Using External Sensors and Joint Angle Sensors,” Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2026), pp. 1445-1450, January 2026 (Cancun, Mexico).
-
Haruto Ueda and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Impact Attenuation in Robotic Hammering Tasks,” Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2026), pp. 1532-1537, January 2026 (Cancun, Mexico).
-
Shouki Miyoshi and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Admittance Control with Independently Designable Task-Space and Joint-Space Dynamics,” a position paper presented at 2025 SICE Festival with Annual Conference (SICE FES 2025), September 2025 (Chiang Mai, Thailand).
-
Myo Thant Sin Aung, Ryo Kikuuwe, Soe Lin Paing, Jun Yang, and Haoyong Yu:“A New Variable-gain Sliding Mode Filter and Its Application to Velocity Filtering,” Proceedings of 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2025), pp. 5601-5607, June 2025 (Atlanta, USA).
|
-
Hanae Yamamoto, Katsuya Kanaoka, and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Torque-based Balancing Control for Teleoperated Bipedal Robots,” Proceedings of the 17th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2025), pp. 722-727, January 2025 (Munich, Germany).
|
 |
-
Yachen Zhang and Ryo Kikuuwe:“Solving Technical Difficulties in Implementing Teleoperated Biped Walking on NAO Robot,” Proceedings of the 16th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2024), pp.1308-1313, January 2024 (Ha Long, Vietnam).
|
 |
-
Yuki Yamamoto and Ryo Kikuuwe:“End-Effector Position Estimation and Control of Hydraulic Excavators with Total Stations,” Proceedings of the 16th IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2024), pp.345-350, January 2024 (Ha Long, Vietnam).
-
Ryo Nishimoto and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Position-Commanding Anti-Sway Controller for Human-Operated Overhead Cranes,” a position paper presented at SICE Annual Conference 2022 (SICE 2022), September 2022 (Kumamoto, Japan).
-
Shih-Ming Wang and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Neural Encoding of Mass Matrices of Articulated Rigid-body Systems in Cholesky-Decomposed Form,” Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT 2022), August 2022.
-
Tomoya Ando, Tomofumi Watari and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Reference ZMP Generation for Teleoperated Bipedal Robots Walking on Non-Flat Terrains,” Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII 2021), pp.794-800, January 2021.
-
Rafael Cisneros, Mehdi Benallegue, Ryo Kikuuwe, Mitsuharu Morisawa, and Fumio Kanehiro: “Reliable Chattering-free Simulation of Friction Torque in Joints Presenting High Stiction,” Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2020), pp.6318-6325, October 2020 (Las Vegas, USA).
-
Shota Sekiguchi and Ryo Kikuuwe: “A Stable Algorithm for Unsolvable Inverse Kinematics of a Class of Six-DoF Manipulators,” Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII 2020), pp.164-169, January 2020 (Hawaii, USA).
-
Tomoya Ando, Tomofumi Watari and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Master-Slave Bipedal Walking and Semi-Automatic Standing Up of Humanoid Robots,” Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII 2020), pp.360-365, January 2020 (Hawaii, USA).
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Rainhart Pasaribu and Gyuho Byun: “A First-Order Differentiator with First-Order Sliding Mode Filtering,” IFAC-PapersOnLine, Vol. 52, Issue 16, Pages 771-776, 2019.
-
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Anti-Noise and Anti-Disturbance Properties of Differential-Algebraic Relaxation Applied to a Set-Valued Controller,” Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Variable Structure Systems and Sliding Mode Control (VSS18), pp.480-485, July 2018 (Graz, Austria).
-
Nehal Baiomy and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An LMI-based Parameter Selection Procedure for an Amplitude- and Rate- Saturated Controller,” Proceedings of the 2018 SICE International Symposium on Control Systems, pp.54-60, March 2018 (Tokyo, Japan)
-
Soe Lin Paing, Myo Thant Sin Aung and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Adaptive Gain Parabolic Sliding Mode Filter Augmented with Vibration Observer,” 1st IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications, pp.602-607, August 2017 (Hawaii, USA).
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Kahhaw Hoo: “A Viscoelastic Tyre Friction Model Based on a Partial Differential-Algebraic Inclusion,” Proceedings in EUROMECH Colloquium 578: Rolling Contact Mechanics for Multibody System Dynamics, April 2017 (Madeira, Portugal). (abstract reviewed)
-
Rafael Cisneros, Ryo Kikuuwe, Shin'ichiro Nakaoka and Fumio Kanehiro: “Stable Simulation of Flexible Cable-Like Objects by Using Serial Kinematic Chains with High Number of Passive Degrees-of-Freedom," In Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots (SIMPAR 2016), pp.119-126, December 2016 (San Francisco, USA).
-
Masayoshi Iwatani and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Elastoplastic Friction Force Estimator and Its Application to External Force Estimation and Force Sensorless Admittance Control,” In Proceedings of 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2016), pp.45-50, December 2016 (Sapporo, Japan).
-
Masayoshi Iwatani and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An External Force Estimator Using Elastoplastic Friction Model With Improved Static Friction Behavior,” In Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV2016), Tu42.6, 2016 (Phuket, Thailand).
-
Masayoshi Iwatani and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Elastoplastic Friction Compensator with Improved Static Friction Behavior,” In Proceedings of SICE Annual Conference 2016 (SICE2016), pp.1091-1097, September 2016 (Tsukuba, Japan).
-
Naoki Wakisaka, Ryo Kikuuwe and Tomomichi Sugihara: “Fast Forward Dynamics Simulation of Robot Manipulators with Highly Frictional Gears,” In Proceedings of 2016 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2016), pp.2096-2101, May 2016 (Stockholm, Sweden).
|
-
Myo Thant Sin Aung and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Acceleration Feedback and Friction Compensation for Improving Positioning Performance in Systems with Friction,” the 2015 American Control Conference (ACC2015), pp.4798-4803, July 2015 (Chicago, USA).
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
High-gain proportional-integral-derivative (PID) position control can achieve stiff position control but it involves the risk of overshoots in some cases such as discontinuous position commands and disturbances. This paper presents a new position controller that achieves accurate trajectory tracking and overdamped resuming motion from large positional errors and disturbances. The proposed controller is a combination of PDD2 (proportional, derivative, and second derivative) controller with nonlinear D2 term, which we call (N-PDD2), and the output of a friction compensator (FC). The nonlinear D2 term allows the use of high gain PDD2 and thus, advantageous in dealing with disturbances. Accurate trajectory-tracking is achieved due to friction compensation. The validity of the proposed controller was demonstrated through experiments in realizing overdamped motion and accurate tracking simultaneously and achieving improvement in robustness to disturbances in a robotic manipulator.
-
Masayoshi Iwatani and Ryo Kikuuwe: “An Identification Procedure for Rate-Dependent Friction Laws of Robotic Manipulator with Limited Motion Range,” In Proceedings of the 10th Asian Control Conference (ASCC2015), pp.526-530, June 2015 (Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia).
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes an identification procedure for rate-dependent friction of robotic manipulators of which the motion is limited due to the configuration or the environment. The procedure is characterized by following three features: (i) the function for the curve fitting is defined by linear interpolation and extrapolation of sampled velocity-force pair points, (ii) each joint is controlled by high gain PID position controller of some cycles of sinusoidal desired trajectory with different frequencies, and (iii) the velocity-force pairs are obtained from each cycle with subtracting the effect of the gravity and the inertia. The procedure was validated with an industrial robotic manipulator YASKAWA MOTOMAN-HP3J, which has six harmonic-drive joints of the reduction ratios of 81.5 to 224. The experimental results show that the procedure has achieved a sufficient accuracy with the 20 degrees of motion of each joint.
-
Myo Thant Sin Aung and Ryo Kikuuwe: “Acceleration Feedback and Friction Compensation for Improving the Stability of Admittance Control,” In Proceedings of the 10th Asian Control Conference (ASCC2015), pp.404-409, June 2015 (Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia).
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper proposes a position control scheme that is suitable for the use as the internal position servo of an admittance controller. The proposed controller is characterized by four points: (a) PDD2 (proportional, derivative, and second derivative) feedback, (b) dither-based friction compensation, (c) sliding-mode-based noise filtering, and (d) variable D2 gain. The PDD2 structure and the friction compensation are theoretically expected to contribute the stability of the admittance control by expanding the bandwidth of the internal position control system. The sliding-mode-based filter is for smoothing the acceleration signals without producing a large phase lag. The variable D2 gain is for reducing the effect of acceleration measurement noise at low velocity. The proposed controller was tested with a 1-DOF device in contact with environments.
-
Myo Thant Sin Aung, Zhan Shi, Ryo Kikuuwe: “A New Noise-Reduction Filter with Sliding Mode and Low-Pass Filtering,” In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Control Applications (CCA), pp.1029-1034, October 2014 (Antibes/Nice, France).
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
This paper presents two contributions in the development of filters for removing high frequency noise. First, three variants of Jin et al.’s (2012) parabolic sliding mode filter (J-PSMF) are derived and their frequency-response characteristics are investigated. Second, a new filter was proposed by combining a second order low-pass filter and one of the variants of J-PSMF. The effectiveness of the proposed filter is validated by using a sample signal of angular velocity obtained with an optical encoder. In particular, it is suggested that the proposed filter has better balance between the noise attenuation and signal preservation than linear low-pass filters and J-PSMF.
|
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Backward-Euler Discretization of Second-Order Sliding Mode Control and Super-Twisting Observer For Accurate Position Control,” In Proceedings of the 2013 ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC 2013), Paper No. DSCC2013-3872, October 2013 (Palo Alto, California, USA).
- [DSCC2013]
- ASME Digital Library
- [Abstract]
This paper introduces an accurate position control algorithm based on Backward-Euler discretization of a second-order sliding mode control (SOSMC) and the super-twisting observer (STO). This position control algorithm does not produce numerical chattering, which has been known to be a major drawback of explicit implementation of SOSMC and STO. It is more accurate than the conventional PID control that is also free of chattering. In contrast to conventional Backward-Euler discretization schemes of SOSMC and STO, the presented discretization method does not require any special solvers for computation. The accuracy and implementation of this algorithm are illustrated by simulations.
|
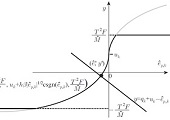 |
-
Shanhai Jin, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Discrete-time Velocity Estimator Based on Sliding Mode and Adaptive Windowing,” In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII 2012), pp.835-841, December 2012 (Fukuoka, Japan).
- IEEE Xplore
- [Abstract]
In position control of mechatronic devices, velocity feedback is necessary for injecting additional damping to avoid low-frequency fluctuation around desired trajectories. In practice, velocity signal is often obtained by performing Euler discretization on position signal from an optical encoder. However, due to the limited encoder resolution, the obtained velocity signal is corrupted by high-frequency noise that may result in high-frequency vibration of the controlled device. This paper presents a discrete-time velocity estimator based on sliding mode and adaptive windowing for position control. Experimental results show that the presented estimator rather improves velocity feedback compared to a sliding mode filter by Jin et al. (2012), an adaptive windowing filter by Janabi-Sharifi et al. (2000), and the cascades of these two filters.
|
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “A Differential-Algebraic Multistate Friction Model,” In Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 7628, Itsuki Noda, Noriaki Ando, Davide Brugali and James J. Kuffner (Eds.), Springer, pp.77-88, 2012. (Proceedings of SIMPAR2012, November 2012, Tsukuba, Japan)
- Springer
- [SIMPAR2012]
- [Abstract]
Fidelity with friction properties and easiness of implementation are both important aspects for friction modeling. Some empirically motivated models can be implemented easily due to their simple expression and small number of parameters, but they cannot capture faithfully the main properties of friction. Some physically motivated models give close agreement with the friction properties, but they can be too complex for some applications. This paper proposes a differential-algebraic multistate friction model that possesses easiness of implementation and adjustment, a relatively small number of parameters and a compact formulation. Moreover, it captures all standard properties of well-established friction models.
|
-
Xiaogang Xiong, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “A Differential-Algebraic Contact Model with Nonlinear Compliance,” In Proceedings of the 2012 ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC/MOVIC 2012), pp. 377-383, October 2012 (Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA).
- ASME Digital Library
- [Abstract]
Modeling of compliant contact is an important issue for simulation and control of mechanical systems. Empirical results in the literature show that, in some mechanical systems such as biological tissues, the relation between the contact force and the indentation is characterized by the following three features: (i) continuity of the force at the time of collision, (ii) Hertz-like nonlinear force-indentation curve, and (iii) non-zero indentation at the time of loss of contact force. The conventional Hunt-Crossley model does not capture the feature (iii) as the model makes the contact force and indentation reach zero simultaneously. This paper proposes a compliant contact model based on a differential-algebraic equation that satisfies all the three features. The behaviors of the model and the effect of parameters in the model are investigated through numerical simulations.
|
-
Shanhai Jin, Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “Improved Velocity Feedback for Position Control by Using a Quadratic Sliding Mode Filter,” In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2011), pp.1207-1212, October 2011 (Goyang, Korea).
-
Ryo Kikuuwe: “Semiglobally Strictly Passive Two-Port Network Representation of Rigid Link Manipulator Under PID Trajectory-Tracking Control,” In Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC 2010), pp.3529-3535, December 2010 (Atlanta, USA).
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Motoji Yamamoto: “A Modular Software Architecture for Simulating Mechanical Systems Involving Coulomb Friction Integrable By the Runge-Kutta Method,” In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2008), pp.2277-2282, September 2008 (Nice, France).
- [pdf file]
©2008 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Naoyuki Takesue and Hideo Fujimoto: “Passive Virtual Fixtures Based on Simulated Position-Dependent Anisotropic Plasticity,” In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2007), pp.3263-3268, April 2007 (Rome, Italy).
- [pdf file]
©2007 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Hideo Fujimoto: “Incorporating Geometric Algorithms in Impedance- and Admittance-Type Haptic Rendering,” In Proceedings of the Second Joint Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems (World Haptics Conference 2007), pp.249-254, March 2007 (Tsukuba, Japan).
- [pdf file]
©2007 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
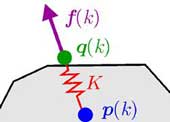 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Takahiro Yamamoto and Hideo Fujimoto: “Velocity-Bounding Stiff Position Controller,” In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2006), pp.3050-3055, October 2006 (Beijing, China).
- [pdf file]
©2006 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
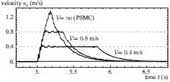 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Yu Kobayashi and Hideo Fujimoto: “Coulomb-Friction-Based Needle Insertion/Withdrawal Model and Its Discrete-Time Implementation,” In Proceedings of EuroHaptics 2006, pp.207-212, July 2006 (Paris, France).
- [pdf file]
- [Abstract]
This paper presents an analytical model of resistance force experienced through a needle when it is being inserted into and withdrawn from membranes. Though the model is based on a very simple assumption of linear elasticity and Coulomb friction, it well captures the `pop' feature, which is a sudden loss of resistance force felt when the needle tip penetrates a membrane. This model describes the needle resistance force as a Coulomb-like friction that involves static friction and kinetic friction. For implementation in haptic devices, a discrete-time representation of this model is derived by using the implicit Euler scheme. The results of implementation experiments using a PHANTOM Omni device are presented.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Hideo Fujimoto: “Proxy-Based Sliding Mode Control For Accurate and Safe Position Control,” In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2006), pp.25-30, May 2006 (Orlando, USA).
- [pdf file]
©2006 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Takahiro Yamamoto and Hideo Fujimoto: “Low-Force Kinesthetic Guidance For Accurate Positioning and Tracking,” In Proceedings of the 14th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems (Haptics 2006), pp.491-498, March 2006 (Alexandria, Virginia, USA).
- [pdf file]
©2006 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
- [pdf of the poster at the conference site]
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Naoyuki Takesue, Akihito Sano, Hiromi Mochiyama and Hideo Fujimoto: “Fixed-Step Friction Simulation: From Classical Coulomb Model to Modern Continuous Models,” In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2005), pp.3910-3917, August 2005 (Edmonton, Canada).
- [pdf file]
©2005 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Akihito Sano, Hiromi Mochiyama, Naoyuki Takesue, Kunihiro Tsunekawa, Sotaro Suzuki and Hideo Fujimoto: “The Tactile Contact Lens,” In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Sensors (SENSORS 2004), pp.535-539, October 2004 (Vienna, Austria).
- [pdf file]
©2004 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
-
Ryo Kikuuwe, Akihito Sano, Hiromi Mochiyama, Naoyuki Takesue and Hideo Fujimoto: “A Tactile Sensor Capable of Mechanical Adaptation and Its Use as a Surface Deflection Detector,” In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Sensors (SENSORS 2004), pp.256-259, October 2004 (Vienna, Austria).
- [pdf file]
©2004 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
 |
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Tsuneo Yoshikawa:
“Recognizing Cylindrical Surface Using Impedance Perception,”
In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003), pp.19-24, October 2003 (Las Vegas, USA).
- [pdf file]
©2003 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
- Ryo Kikuuwe and Tsuneo Yoshikawa:
“Recognizing Surface Properties Using Impedance Perception,”
In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2003), pp.1539-1544, September 2003 (Taipei, Taiwan).
- [pdf file]
©2003 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
- Ryo Kikuuwe and Tsuneo Yoshikawa: “Robot Perception of Environment Impedance,” In Proceedings of 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2002), pp.1661-1666, May 2002 (Washington DC, USA).
- [pdf file]
©2002 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
-
Ryo Kikuuwe and Tsuneo Yoshikawa: “Haptic Display Device with Fingertip Presser for Motion/Force Teaching to Human,” In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2001), pp.868-873, May 2001 (Seoul, Korea).
- [pdf file]
©2001 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
 |
 or send me a request from ResearchGate.
or send me a request from ResearchGate.